Funded by the UK’s United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research, we are an experienced group of researchers with wide-ranging skills: epidemiology, clinical medicine, social sciences and anthropology, clinical trials, health economics, public health, laboratory sciences and diagnostics. Together, we will take a broad approach to the common problem of skin disease to help deliver healthy skin and healthy lives.
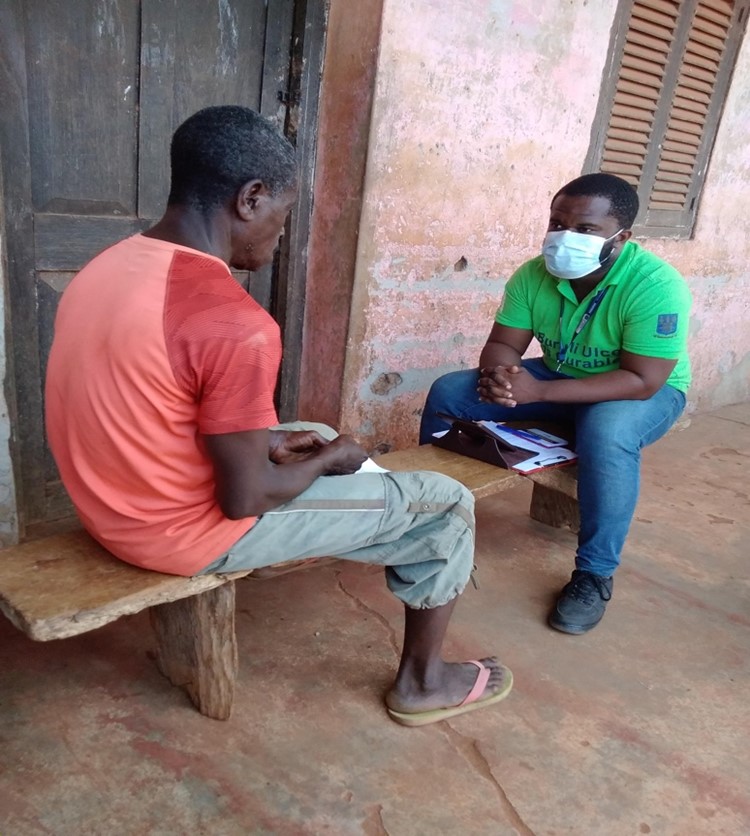
Neglected tropical diseases of the skin - such as Buruli ulcer, cutaneous leishmaniasis, leprosy, and yaws - are associated with physical disability, psychological distress, financial hardship, and social isolation. Conducted with affected individuals, communities, and other stakeholders, our research programme comprises three projects in Ethiopia and Ghana.
Working in Partnership in Ghana and Ethiopia
The Skin Health Africa Research Programme (SHARP) is a collaboration between the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, the University of Ghana, the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (Ghana), the Addis Ababa University, and the Armauer Hansen Research Institute (Ethiopia). We are an experienced group of researchers with wide-ranging skills: epidemiology, clinical medicine, social sciences and anthropology, clinical trials, health economics, public health, laboratory sciences and diagnostics. Together, we take a broad approach to the common problem of skin disease to help deliver healthy skin and healthy lives.
Funding
SHARP is funded by the United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research via the Research and Innovation for Global Health Transformation (RIGHT) scheme (2019-2023).
We are an experienced group of researchers with wide-ranging skills: epidemiology, clinical medicine, social sciences and anthropology, clinical trials, health economics, public health, laboratory sciences and diagnostics.
A full list of our team members will be added soon. For now, we include the lead investigator at each of our five partner institutions:
London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, United Kingdom
Kumasi Centre for Collaborative Research in Tropical Medicine, Ghana
Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, University of Ghana
Armauer Hansen Research Institute, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia
Aim
The programme aims to identify strategies for improving experiences of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) of the skin which are severe and stigmatising.
Rationale
Skin disease is a leading cause of global chronic disease burden and morbidity. Skin NTDs such as Buruli ulcer, cutaneous leishmaniasis, leprosy and yaws are associated with physical disability, psychological distress, financial hardship and social isolation. In communities affected by skin NTDs there is also an enormous burden of other skin diseases caused by other infections which needs to be addressed. These more common diseases of the skin are also associated with stigma and reduced quality of life and may confound the diagnosis of skin NTDs.
The World Health Organization has identified opportunities for combining efforts to identify and manage different skin NTDs and has developed training guides for health workers. One rationale for a combined or “integrated” approach is that the implementation of two or more skin NTD-related activities in communities should be a more efficient use of scarce resources. An integrated approach to skin NTDs which tackles more common skin diseases may be more acceptable and have greater impact. The best strategies to diagnose and treat multiple NTDs affecting the skin in a single programme need to be identified.
Our activities
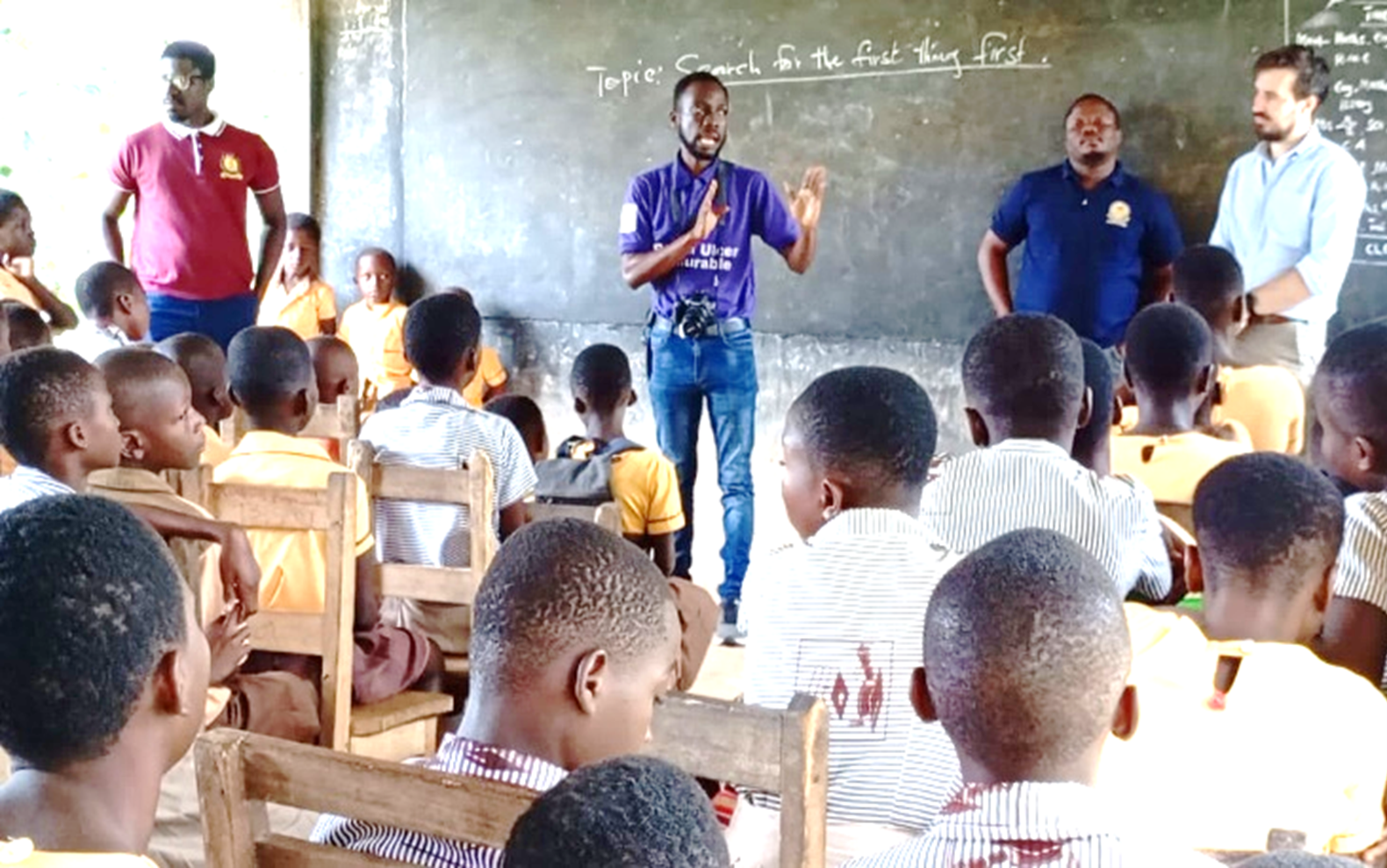
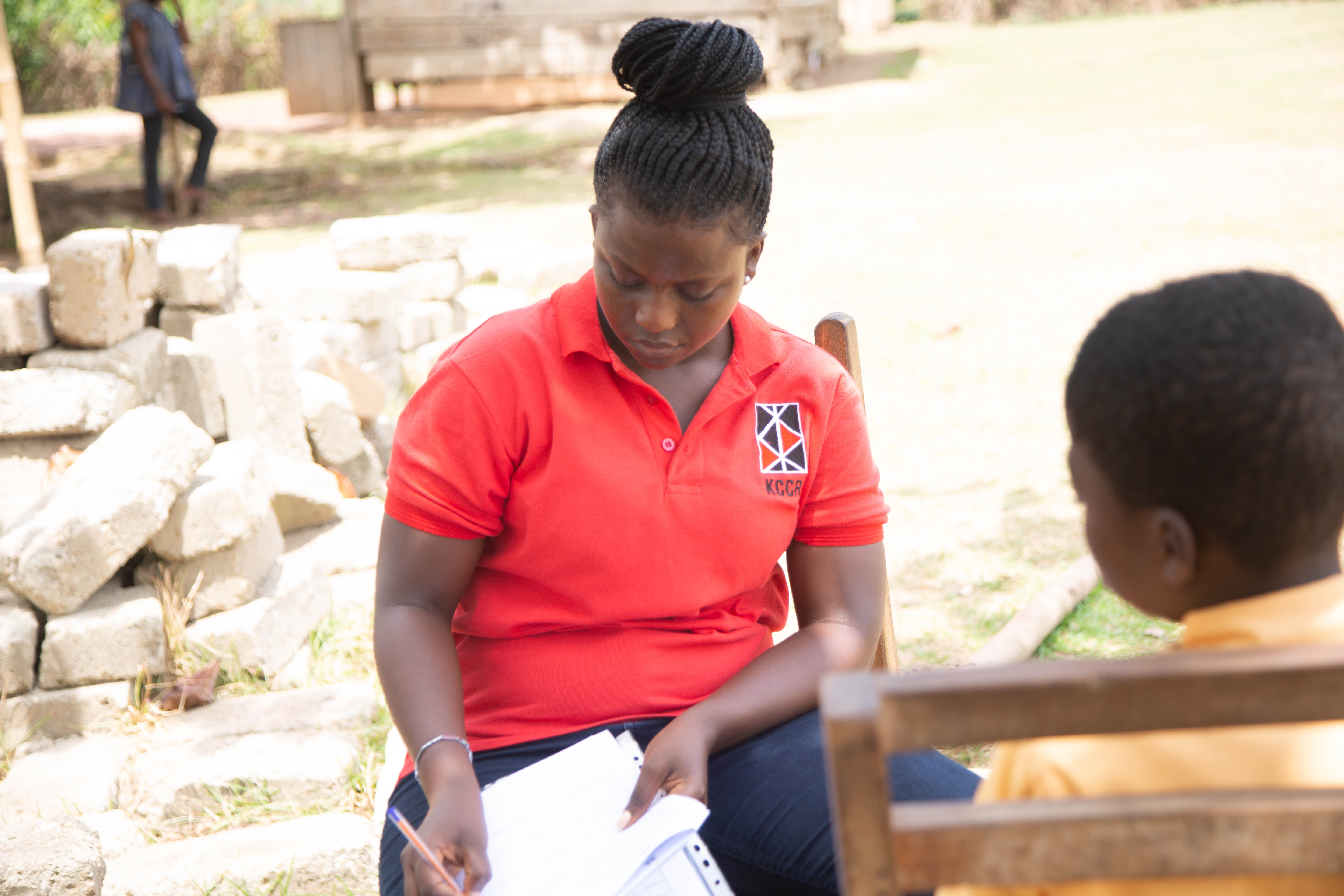
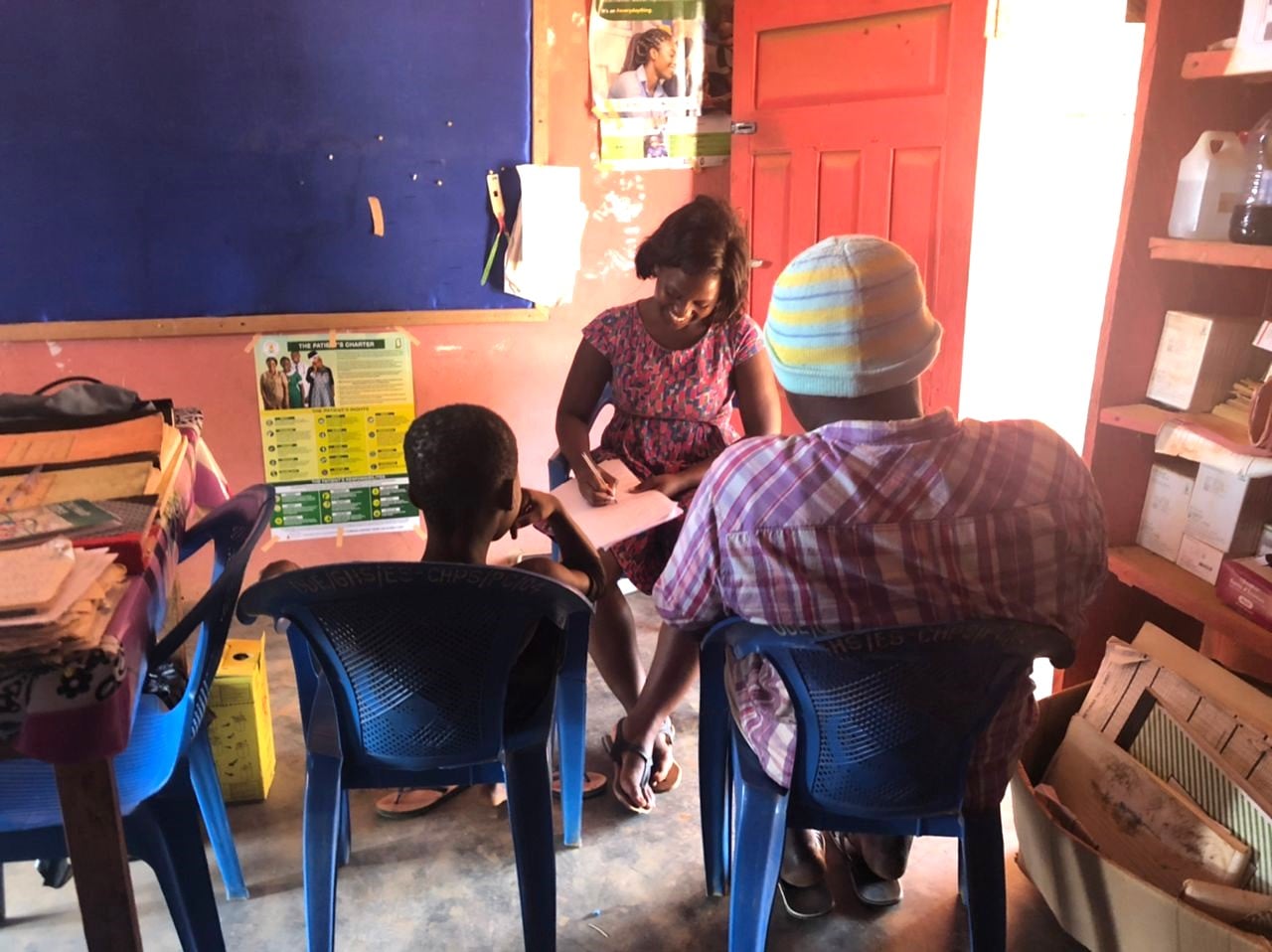
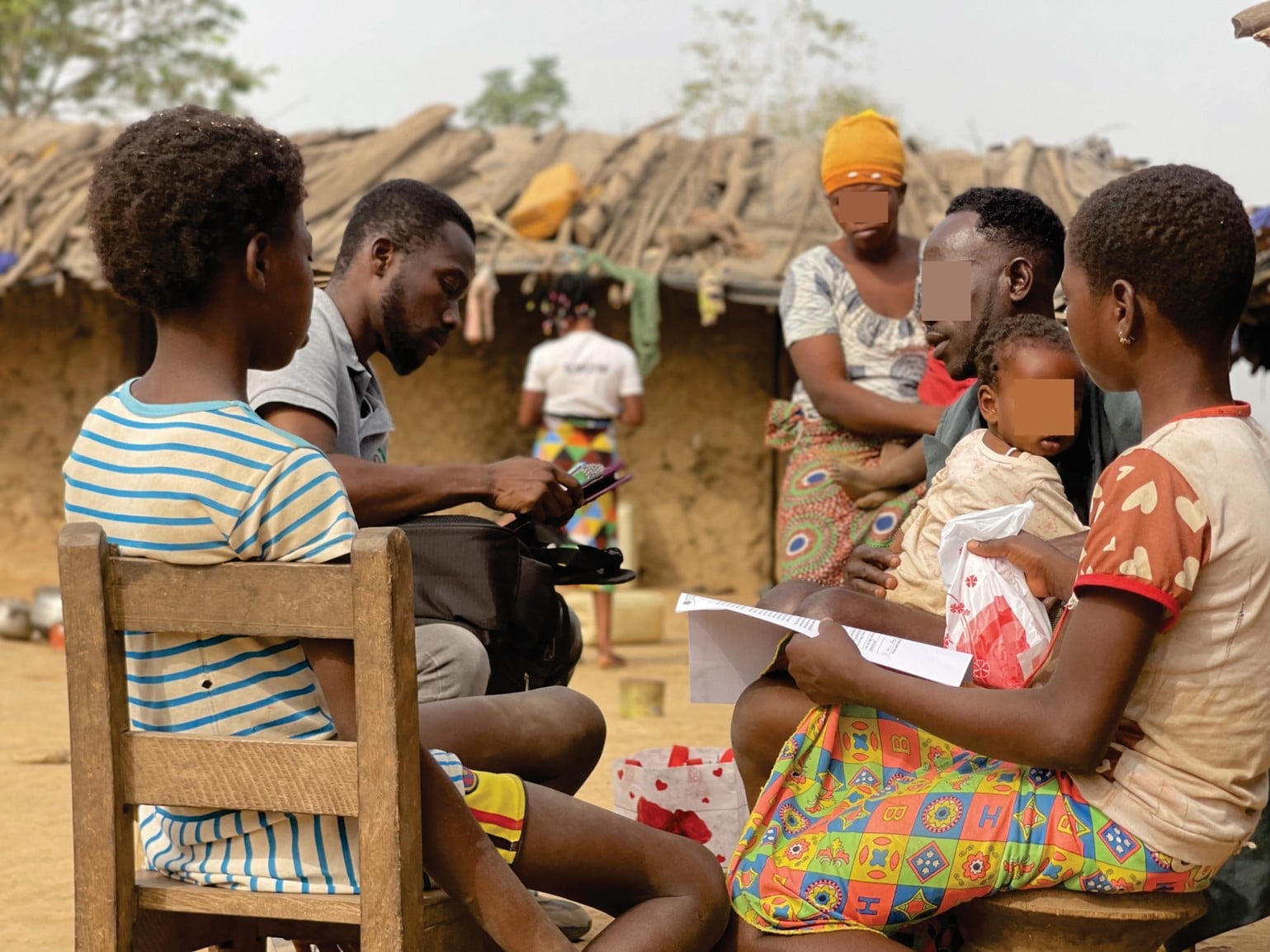
Conducted with affected individuals, communities, and other stakeholders, our research programme comprises three projects:
- A randomised-controlled trial to compare the effects of a novel wound dressing on the healing of Buruli ulcer in Ghana
- A cohort study of individuals diagnosed with cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia
- Development and testing of active case finding systems for skin NTDs in Ghana and Ethiopia
Three themes cut across all our work:
- Understanding and addressing stigma
- Capacity building
- Economic evaluation
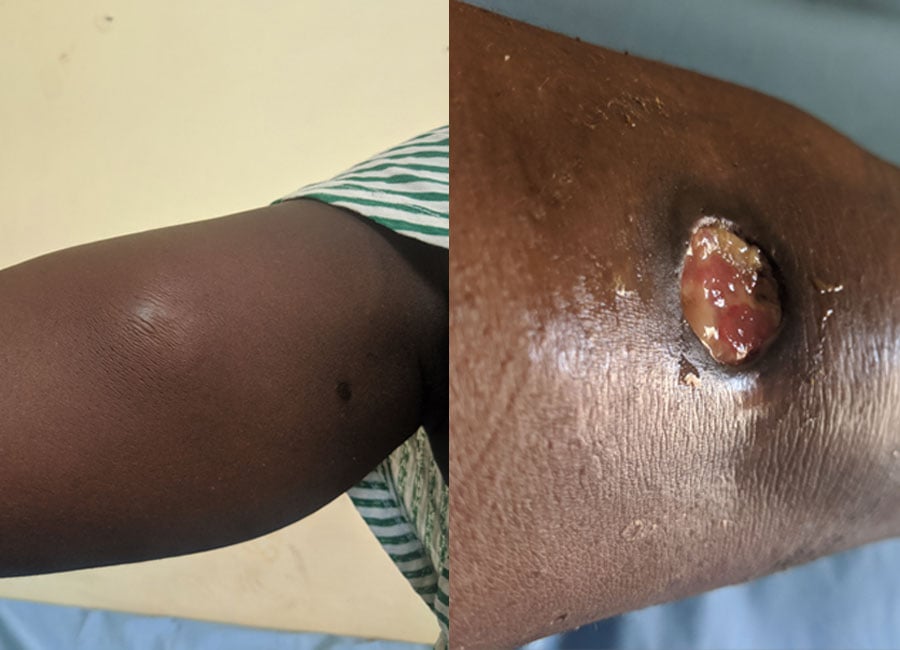
If untreated, early Buruli ulcers can progress to large ulcers which may involve the whole limb. With antibiotic treatment and good wound care patients can make an excellent recovery.
Through our research, we have produced some helpful resources.
The following resources provide further information on neglected tropical diseases of the skin:
- ENLIST - The Erythema Nodosum Leprosum International Study group
- International Alliance for the Control of Scabies
- International Foundation for Dermatology
- London Centre for Neglected Tropical Disease Research
- Neglected Tropical Diseases Modelling Consortium
- Tropical Dermatology Short Course at LSHTM
- World Health Organization resources on skin NTDs, including pictorial training guide
Tell us a bit about your background and career before SHARP
I joined the school as a research fellow in health economics in 2021, after 2 years as a teaching fellow in the Department of Health Policy at the LSE. Prior to that, my previous role as a Research Associate with King’s College London, focused on the economic evaluation of interventions in both physical and mental health. My past work experience includes a researcher role at the Ministry of Health in Botswana on projects evaluating the health financing system and assessing national health accounts. I work on the cost-effectiveness of interventions within randomised controlled trials and apply decision modelling techniques. My interest extends to adapting and applying health economics methods in low- and middle-income countries, and to support this, I published a book chapter, assessing economic evaluations in global mental health.
What has been your specific role in SHARP, and what studies have you worked on?
As a health economist, my primary role in SHARP has been supporting the development and implementation of economic studies of the programme, including a systematic review of economic evaluations of interventions for Neglected Tropical Skin Diseases, and two conceptual models for assessing the cost-effectiveness of integrated case finding and management strategies for NTDs and for integrated case finding and management strategies for NTDs.
How has it been collaborating with the partner institutions that make up SHARP?
Collaborating with partner institutions in Ghana and Ethiopia has led to the exchange of diverse ideas and approaches, fostering creativity and innovation in SHARP. Combining strengths from multiple institutions has also contributed to higher-quality research and outcomes. This collaboration has also provided opportunities for mutual learning and enriched knowledge exchange.
What do you hope the legacy of SHARP will be, and what will you be working on next?
Overall, I think SHARP will Improve access to quality care of skin NTDs in the countries of study. Given the scarcity of conceptual models for economic evaluations in skin NTDs, I hope our case study will act as guidance and promote wider use of the approach.
What message would you give to other ECRs aspiring to a career in research?
Navigating this phase requires focusing on developing strong methodological skills, publishing strategically and regularly presenting your research at conferences and seminars. This improves your communication skills and increases the visibility of your work. It is also vital to take advantage of professional development opportunities. Attend workshops on grant writing, teaching, and career planning.
I have greatly enjoyed collaborating with the multi-disciplinary team on SHARP and am excited to see its impact on the future of skin NTDs.
Members of SHARP, including researchers from the Global Health Economics Centre at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, showed that NTDs of the skin can have significant financial and economic burdens on individuals and households, particularly the poorest, both through the direct costs of care-seeking and loss of income.
Tell us a bit about your background and career before SHARP
In 2012, I completed my undergraduate studies in sociology and philosophy at the University of Ghana. In 2013, I began my required one-year National Service at the Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research (NMIMR), working on the Wellcome Trust Tuberculosis project under the direction of Professors Dorothy Yeboah-Manu and Collins Ahorlu. During this time, I worked on patient interviews, data entry, sample transportation from medical institutions to NMIMR laboratories, and data analysis.
After my service, I continued to work with the Dorothy-Yeboah Manu group as a Research Assistant for Dr. Eric Koka on the ‘Stop BU’ project (2013-2016).
I voluntarily worked with the Epidemiology Department under the supervision of Prof. Ahorlu between 2018 and 2020 while exploring other research employment opportunities. From 2021 till date, I have worked extensively on the SHARP project as a research assistant, supporting the team with my experience in social epidemiology.
What has been your specific role in SHARP, and what studies have you worked on?
As part of SHARP, I was involved in data collection and analysis during the formative aspect of the SHARP project which led to the development of a complex intervention in Atwima Mponua district of the Ashanti Region of Ghana. With support from other teammates, I led the publication of a paper to disseminate the findings of the formative work. I also worked on drafting of two more papers on the SHARP project. I was heavily involved in the data collection methods employed on the project including IDIs, FGDs, ethnography; leading community entry and co-creation workshops; and data analysis.
How has it been collaborating with the partner institutions that make up SHARP?
It's been fantastic! With excellent communication and contributions from all institutions, the partnership has been fruitful and enjoyable. Having team members to work with has been great. Our outstanding collaboration has allowed us to share knowledge and insights that have greatly enhanced the SHARP project.
What do you hope the legacy of SHARP will be, and what will you be working on next?
It is my hope that SHARP's legacy will have a long-lasting effect on the lives of people in the Atwima Mponua district who have to cope with skin NTDs and other skin problems. I’m really enthused about how SHARP will expand knowledge of science and develop fruitful partnerships with NMIMR so that we may expand our interventions to other regions of Ghana globe.
Next, I'll be focusing on furthering my research in how the health facilities in the district will cope with the reality of health service delivery after the intervention period and exploring new opportunities for innovation and growth for people living with NTDs.
What message would you give to other ECRs aspiring to a career in research?
My message to early career researchers is very simple. Embarking on a research career is both a challenging and rewarding journey. One needs to stay curious and persistent while building a strong network to effectively communicate your findings. Early Career Researchers have to embrace failures as learning opportunities, balance dedication with self-care, and always let your passion drive you.
Remember, your work has the potential to contribute significantly to the body of knowledge and make a real-world impact. Stay dedicated, keep learning, and believe in your ability to make a difference.
I am very grateful to my mentors and supervisors at NMIMR; Prof Dorothy Yeboah-Manu, Prof. Collins Ahorlu, Dr. Adwoa Asante-Poku, Dr Eric Koka and Dr Richard Adjei Akuffo for their immense support and leadership roles in my career path. Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research is a great place for early career researchers to nurture their enthusiasm for the future when it comes to research. ‘Noguchi Excellence…Working as a Team’.
Tell us a bit about your background and career before SHARP
Before SHARP, I studied Public Health, Health Education and Promotion at Jimma University (Ethiopia), and subsequently worked in higher educational institutions as a lecturer and researcher for more than 15 years. I’m currently an Assistant Professor at St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College with focus on health promotion and communication, and a PhD student at Addis Ababa University, School of Public Health.
What has been your specific role in SHARP?
I joined SHARP to collaborate with the partner institutions and conduct my PhD Dissertation project on Community Engagement for Co-creation of Educational Materials and Improved Service Uptake for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (CL) in Ethiopia.
The community dialogue intervention focus on creating awareness on CL to minimize misconceptions/misunderstanding related to cause, transmission, and risk factors for exposure to CL, co-create health messages through community dialogue approach, and recruit and engage ‘CL champions’ to create awareness on CL, support and link people suspected to have CL to health facilities.
How has it been collaborating with the partner institutions that make up SHARP?
Graciously, collaborating with the partner institutions that make up SHARP, particularly, Addis Ababa University, Armauer Hansen Research Institute (AHRI), London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) is great. I appreciate the collaborative work among these institutions to address severe stigmatizing skin diseases (SSSDs), particularly CL in Ethiopia. I was very happy with the financial and technical support from the SHARP team. We are doing great work to minimize misconceptions and stigma associated with CL in the intervention community. Above all, this gives mental satisfaction for the team members because CL, as an NTD, did not get full attention previously. I am very happy to be part of this inspiring project and I have learned a lot.
What do you hope the legacy of SHARP will be?
That misconceptions of the cause, transmission and risk of exposures of CL and associated stigma will be minimized. I hope lessons learned and materials created from this project will inform efforts to engage communities and improve access to quality care for CL and other skin problems in Ethiopia and beyond. Of course, SHARP is also generating scientific evidence through the collaborative works, which will help researchers and academics in the field to perform evidence-based interventions.
What message would you give to other ECRs aspiring to a career in research?
My message to other early career researchers aspiring to a career in research would be collaborate and engage with the broader research. Networking opens doors to new ideas, opportunities, and support systems crucial for research success. You collaborate with supportive mentors and colleagues who can guide and inspire you along the way. These are the benefit I got by collaborating with SHARP project multidisciplinary teams while I am working on a career in research.
Finally, I just want to say that I am fortunate! As a young scientist from Ethiopia, a developing country, getting this support From SHARP Project has greatly empowered me. Conducting this research will enhance my skills and knowledge. It will provide advanced experience in conducting implementation research towards my long-term goal of becoming an established independent researcher in implementation science. I will have an opportunity to conduct research that will have a great impact locally and worldwide.
One of the main effects of skin neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) on individuals, alongside direct effects on health, is that of stigmatisation. SHARP scientists conducted research, published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, in two central districts in Ghana and demonstrated how stigma impacts individuals with Yaws and Buruli ulcer differently, highlighting disease-specific nuances and how stigma varies by age group.
Skin NTDs, by their nature, attract stigmatisation. They are often visually apparent and are regularly nested within negative cultural and societal perceptions and beliefs.
While the World Health Organization (WHO) has issued a call for integrated disease management of skin NTDs, there isn’t an abundance of research on the particulars of how stigma affects different individuals, and different types of skin NTDs.
SHARP has found that stigma experiences had notable negative consequences on psychosocial well-being, schooling, and social relations, particularly for individuals affected by Buruli ulcer, and in a more direct way for younger study participants.
Dr Yaw Amoako, Senior Specialist Infectious Diseases Physician and Research Scientist at KCCR said, "Our work on stigma provides evidence on the interplay and nuances between stigma experiences, effects and coping strategies employed by people affected with different skin NTDs.
“Our evidence on how stigma may affect people of differing age groups is crucial to tailor context-specific intervention packages for people affected by skin NTDs."
Defining stigma
Much modern research on stigma has roots in Goffman’s treatise on stigma. Goffman defines stigma as the reaction to an ‘undesired differentness from what we had anticipated’. It’s how a perception (either from themself or from others) of an individual differs from societal norms in a negative way.
To fully understand this phenomenon, SHARP researchers broke their study of stigma down into different parts. This includes macro stigma, micro stigma, the effects of stigmatisation, and coping strategies used by individuals. The framework for this semi-structured interview format is available online.
Macro stigma is what likely first springs to mind when stigma is discussed. It is what you see when you take a broad look at society and includes actions such as teasing, avoidance, or exclusion of affected individuals by their peers. Micro stigma, on the other hand, focuses on the individual and includes self-isolation, and how an individual perceives others’ views of them.
A novel approach
Ideally, healthcare systems need to be adaptable to the specific needs of individuals. A successful intervention, therefore, must be informed by these nuances.
SHARP’s study provides two important insights. Firstly, differences between yaws and Buruli ulcer. For example, yaws lesions tend to be smaller and less disfiguring than BU ulcers and so induce less stigma and be socially acceptable. This logic is supported by the finding that non-ulcerated forms of BU were associated with less stigma than large ulcers.
Secondly, the study looks closely at how age affects stigma. Older participants and caregivers mainly discussed the pain of dealing with public staring, and more subtle experiences than younger participants.
“People can stare at me because I think they wonder why such an old person like me has a bandage on her leg. Especially, when I walk around with my stick, I bow down my head, they can stare at you for such a long time” - 60-year-old female, formerly affected with BU.
On the other hand, younger participants shared more direct experiences of stigma, such as teasing and name-calling.
“…when I leave it [ulcer] open without dressing it, some people will see me and say, [referring to the ulcer] look at the torch … it made me feel very sad, there were even times that I cry when they say that.
“Before I had BU, my classmates were close to me, but after I had the condition, they were afraid that they will get infected if they come closer to me. When I go to school, all the pupils do not want to get closer to me” - 11-year-old female, formerly affected with BU
Hearing the experiences of young people was particularly revealing, as exclusionary behaviour was enacted not only by other students, but by some teachers and school food vendors too.
Learning this is important, and feeds into SHARP’s intervention development. If some teachers are perpetuating stigma through ignorance of these diseases, they must be included in the development of interventions. As teachers are widely regarded as champions of the community, it is vital that they do not become agents of stigma.
A deeper understanding of stigma, and its effect on individuals, is integral to creating a robust and effective intervention that considers the intersection of different patient’s needs.
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are diseases that are largely absent from the global health agenda and often result in stigma and social exclusion. Yaws, Buruli Ulcer, and Leprosy are examples of skin NTDs that the Skin Health Africa Research Programme (SHARP) research, and all three are associated with physical disability, psychological distress, financial hardship, and social isolation. These diseases are caused by bacterial infection of the skin and surrounding tissues, but while effective cures exist, systemic and social barriers can prevent the access to care that affected individuals need.
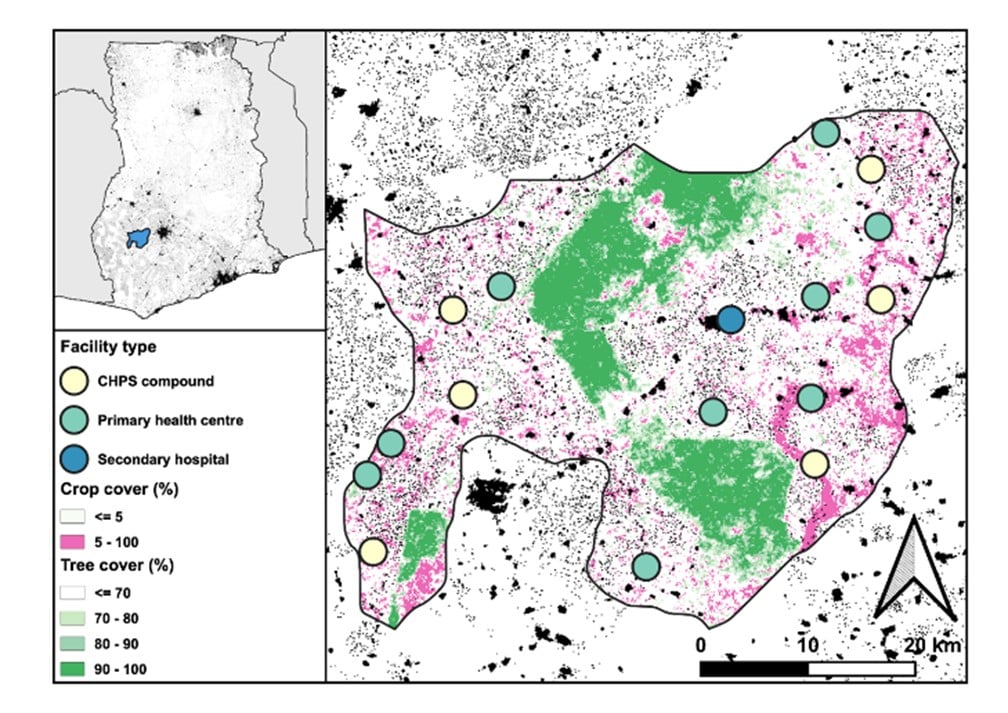
In 2021, the Ghana Health Service updated its Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) Masterplan. This initiative from the Ghana Health Service promotes integration of previously disease-specific, centralised programmes within regular primary healthcare services. Implementing this new style of programming to manage NTDs of the skin is complicated and requires tailoring to local contexts.
To support this, researchers from SHARP have conducted extensive research with community members in Atwima Mponua District in Ghana’s Ashanti Region to explore people’s routes into and through care systems with the goal of implementing effective interventions to help management of skin NTDs. This work has now been published in PLOS Global Public Health for both formative research and intervention development.
Dr Jennifer Palmer, one of the study’s co-authors from LSHTM noted, “To date, investment in skin NTDs in Ghana has been focused in other areas of the country, while this really rural district, Atwima Mponua, has not benefited from any specific skin NTDs programming. This lack of investment was very evident once we began engaging with health workers.”
Understanding the problem
The team sought to investigate the local health system’s readiness to provide care, as well as the local community’s perceptions and experiences of skin NTDs and services. In doing so, SHARP was able to uncover what existing good practices there are that can be preserved and built on, as well as what needs to change.
To do this, SHARP’s study brought together diverse skillsets from The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, Kumasi Centre for Collaborative Research in Tropical Medicine, and The Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research. Together, they used a variety of techniques from open-ended interviews to more structured enquiries about health facilities to inform on possible interventions and understand common skin NTD care-seeking practices in the district.
The team took a holistic bottom-up approach involving group discussions with community members, plentiful and varied stakeholder meetings, and engaging with health workers. The aim was to not only understand what strategies are employed to detect skin NTD cases, and their understanding of stigma, but also how affected people and communities use the health system within a context of plural medicine. Expanding on this, SHARP have also conducted an in-depth study of skin NTD stigma, published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, and we will be sharing an article delving deeper into the topic on our website soon.
Prof. Dorothy Yeboah-Manu, Director of the Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research said, “Our initial research in the Atwima Mponua District of Ghana provided context about the burden of skin NTDs and people’s lived experiences.
“Engagement helped us to re-orient our initial ideas to align with the needs of the people and to start developing a new decentralised skin health care model."
Developing the intervention
Initial research made it clear that there was a lack of previous skin NTDs programming investment in district health facilities. Key health workers described not really knowing how to manage skin NTDs and simply referred people who might need care to hospitals outside the district. This meant a key task for SHARP was to break down diagnostic and treatment processes for primary healthcare level implementation.
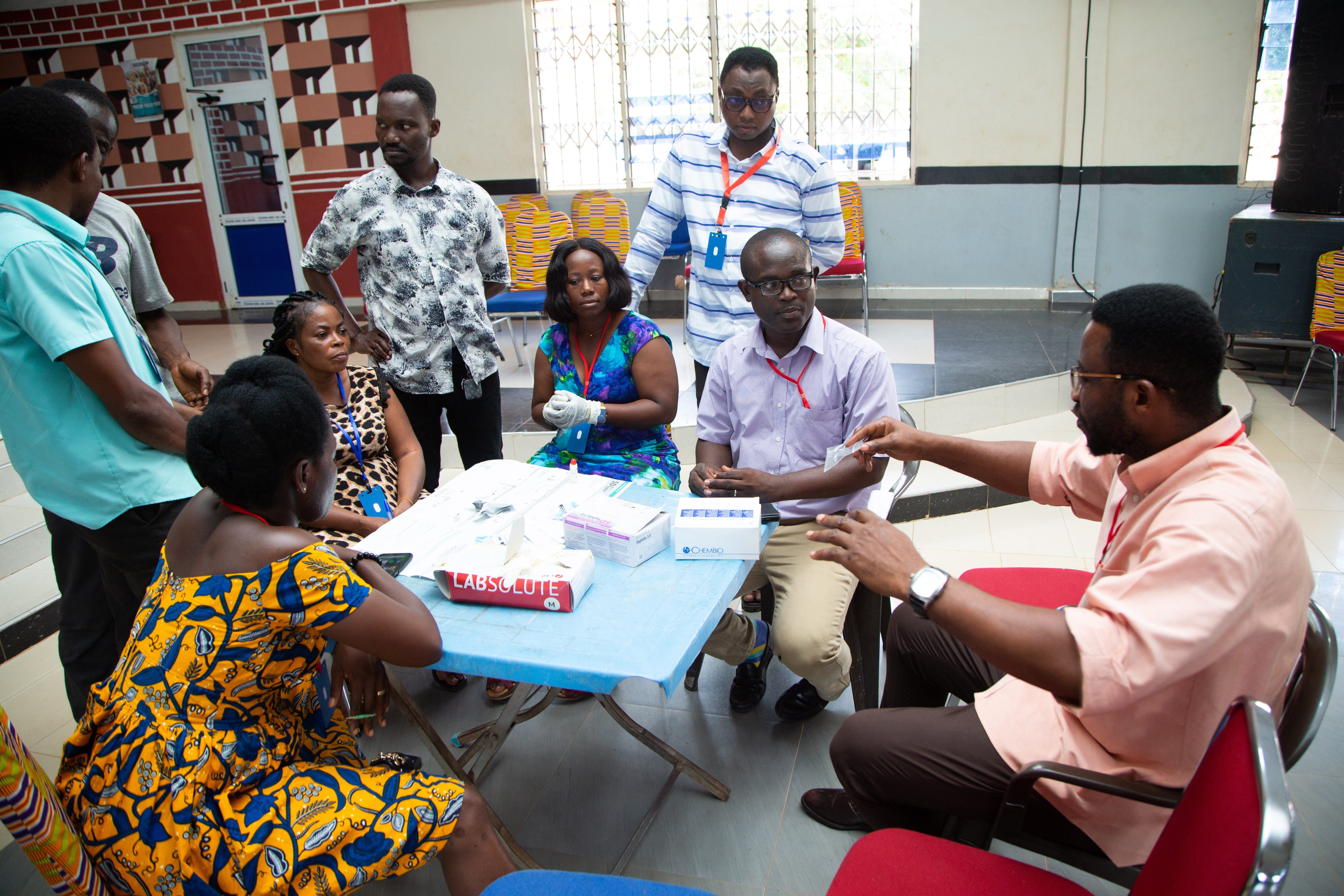
Using yaws as an example, it is treatable with a single dose of azithromycin, commonly available in frontline facilities and diagnosable with the same rapid test used for syphilis screening. With all the tools for effective treatment already there, the next step is working with health authorities and facility managers to communicate that these diagnostics and medicines can be used for this purpose, and training frontline staff to recognise the signs of yaws to know when to use them.
Another example, for Buruli ulcer, is that there was no systematic way to send samples for testing at regional labs. Instead, health workers used personal connections with lab staff at KCCR for sample testing. It therefore made sense that the intervention included formalising the sample testing pathway, pre-positioning necessary supplies, and expanding existing WhatsApp groups to facilitate sample transportation.
In co-development workshops, stakeholders agreed that addressing skin conditions and wounds comprehensively, rather than focusing solely on skin NTDs, would be more effective. This broader focus on skin health was seen as more acceptable to the population, likely to encourage timely care-seeking behaviour, and could offer an efficient method for improving overall health and strengthening health service delivery.
The co-development process also facilitated the identification of practical solutions that considered local contexts and resources. For example, a training and support package for health worker supervision of home-based care for some wounds was introduced to build on an existing practice of home management. Government stakeholders also prioritised a strategy that would not rely on external funding, emphasising the importance of sustainability and local ownership. This participatory approach ensured that the proposed strategy could be feasibly implemented by the district health management team within the study district and had the potential for scalability if successful.
By engaging diverse perspectives, the co-development workshops promoted a more inclusive and well-rounded strategy, enhancing the likelihood of its success and sustainability in creating impactful change for people suffering with skin NTDs.
On the first World NTD Day, Steve Walker presented about SHARP at an event organized by the London Centre for Neglected Tropical Disease Research (LCNTDR). The gathering included more than 145 attendees and a keynote address by Catherine West, a member of parliament and chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group for Malaria and NTDs.
Read more about the World NTD Day.
The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) is to co-lead a major new project to identify the best ways to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life of people with neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) of the skin.
Read more about the £5 million project.
The SHARP team held highly productive meetings in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 2-3 December and in Accra, Ghana on 5-6 December, 2019 to kick off the research programme. Members of the LSHTM team first joined researchers from AHRI and Addis Ababa University for a two-day meeting in Addis before flying to Accra for a second two-day meeting with researchers from KNUST/KCCR and the Noguchi Memorial Institute at the University of Ghana. While some members of the team are longstanding collaborators, these face-to-face meetings also allowed other members of the team to meet one another for the first time. Presentations were given on all aspects of the research programme and plans agreed for how to take the research forwards. External stakeholders participated in both meetings and provided valuable guidance on how to ensure that the research programme produces positive change for individuals and communities affected by neglected tropical diseases of the skin.